☝️ At a glance
- Becoming a doctor in India involves the NEET exam, completing an MBBS degree, and obtaining registration.
- Eligibility requires completing secondary education with Physics, Chemistry, and Biology.
- NEET is crucial for medical college admission and demands thorough preparation. Choosing a college involves weighing government versus private options, fees, and career prospects.
- The five-and-a-half-year MBBS program, including an internship, leads to a medical license and opens careers in hospitals, private practice, research, or academia.
To become a doctor in India is a dream shared by many young students and their families. This profession is not only prestigious but also offers the opportunity to make a significant impact on society by improving health outcomes and saving lives.
However, the journey to becoming an MBBS doctor in India is long and demands unwavering dedication, perseverance, and a deep passion for medicine. Whether you're aiming for a medical degree from a top college or looking to explore diverse career opportunities within the medical field, this comprehensive guide will walk you through each step-from choosing the right college to obtaining your license to practice medicine in India.

Step 1: Preparing for medical school
Understanding the eligibility criteria
Before starting the journey of how to become a doctor in India, the first step is to understand and meet the eligibility criteria for MBBS admission to medical institutions across the country. Generally, this includes completing your secondary education (Class 12) with a focus on the science stream. Key subjects like Physics, Chemistry, and Biology are crucial, as they lay the groundwork for your understanding of medical sciences. Your performance in these subjects is vital as it directly impacts your chances of gaining admission to a reputable college.
To be eligible for the NEET exam, candidates must meet the following academic requirements as they form the foundation for your medical education, leading you to become a doctor in India.:
- Class 12 board examinations: Must have passed with at least 50% aggregate marks in Physics, Chemistry, and Biology.
- Reserved categories: Minimum required marks are 40% in Physics, Chemistry, and Biology.
- Mandatory subject: English is also required in Class 12.
Importance of the science stream
Choosing the science stream during your secondary education is a pivotal decision that lays the groundwork for your journey into the medical field. The subjects of Physics, Chemistry, and Biology are not just important for entrance exams like NEET, but they are also central to the MBBS courses you'll undertake in medical school. Excelling in these subjects gives you a strong foundation in the basic sciences, which is essential for grasping the complex concepts in medical sciences. Moreover, a solid understanding of these subjects will help you perform better in the NEET exam, which is the gateway to securing admission in a top college. From there, it's just a few more years of dedicated study before you achieve your goal of becoming a doctor in India.
Click here to download the NEET Zoology chapter-wise weightage
Download PDF
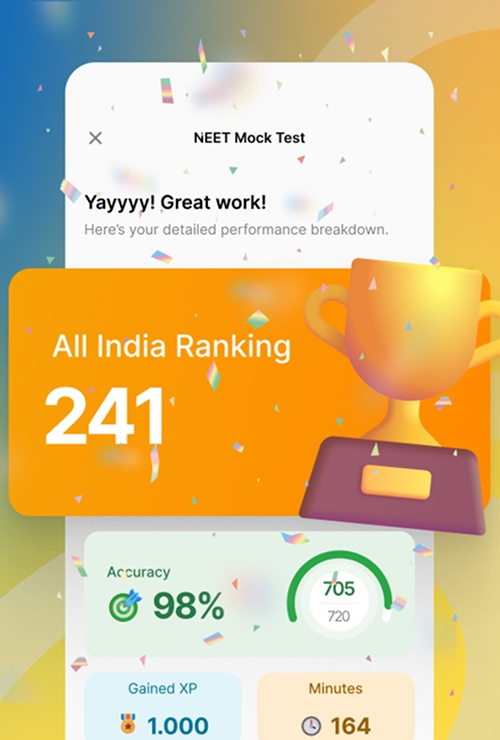
Step 2: Clearing the NEET exam
National Eligibility Entrance Test (NEET)
The National Eligibility Entrance Test (NEET) is a nationwide entrance exam that aspiring doctors must clear to secure admission to undergraduate medical courses like MBBS and BDS (Bachelor of Dental Surgery) in India. It is one of the most competitive exams in the country, with lots of students appearing each year for a limited number of seats in medical schools. Scoring well in NEET exam is crucial as it determines your chances of securing a seat in a reputed medical school and is a key part of the admission procedure. Understanding how to become a doctor in India hinges on performing well in this exam, as it is a significant step towards becoming an MBBS doctor.
The NEET exam comprises questions from Physics, Chemistry, and Biology (Botany and Zoology). The exam is designed to test your understanding of these subjects at a high level, making thorough preparation essential. The importance of the NEET cannot be overstated, as it is the primary determinant of your ability to pursue MBBS and ultimately become a doctor in India. NEETsheet offers high-quality preparation with resources from India's best Ed-Tech teachers, designed specifically to produce top NEET rankers. With a proven track record of success, NEETsheet enhances your study efficiency and significantly boosts your chances of achieving a top score on the exam.
NEET exam preparation tips
Preparing for the NEET exams requires a well-planned strategy, consistent effort, and a deep understanding of the subjects. Here are some tips to help you succeed:
- Master the basics: Ensure that your basics in Physics, Chemistry, and Biology are strong. These subjects form the core of the NEET syllabus, and a solid foundation is essential for success in medical courses.
- Practice regularly: Regular practice through mock tests and previous years' question papers can help you get accustomed to the entrance exam pattern and improve your time management skills.
- Stay updated: Keep yourself updated with the latest NEET syllabus and exam pattern. Any changes in the exam structure should be noted and incorporated into your preparation plan.
- Focus on weak areas: Identify your weak areas and dedicate extra time to improving them. Strengthening these areas can significantly boost your overall score.
- Join coaching classes: Many students benefit from joining coaching classes that specialize in NEET exams preparation. These classes provide structured guidance, study material, and mock tests that can enhance your preparation.
The NEET exams are a significant milestone in "how to become a doctor in India", and with the right preparation, you can achieve the score required to secure admission to a top college.
NEET exam structure
Feature | Details |
Mode | Pen and Paper-Based Test |
Duration | 3 hours |
Total marks | 720 |
Questions | 200 (50 each in Physics, Chemistry, Biology) |
Marking scheme | +4 for correct, -1 for incorrect |
Subjects | Physics, Chemistry, Biology |
Syllabus | NCERT Class 11 & 12 textbooks |
Step 3: Choosing the right medical college
Top MBBS colleges in India
Choosing the right college is an important decision you will make on your path of "how to become a doctor in India". Opportunities for hands-on-experience, and your future career prospects shall be influenced majorly by the college you choose. It is known that India is home to some of the world's best medical institutions , offering quality education, state-of-the-art facilities, and experienced faculty.
Here are some of the top MBBS colleges in India:
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), Delhi: AIIMS Delhi is the premier medical institute in India, renowned for its cutting-edge research, world-class faculty, and top-tier education. Vast opportunities in Clinical exposure, research, and specialized training make it the top choice for aspiring doctors.
- Kasturba Medical College (KMC), Manipal: KMC is one of the first private medical college in India, renowned for its world-class infrastructure and innovative teaching methods. A wide range of undergraduate degree and postgraduate medical programs, are offered to students attracting them from across the globe.
- Christian Medical College (CMC), Vellore: CMC Vellore is one of the oldest and most prestigious medical schools in India. High-quality education and healthcare services are the norm here.
These top medical colleges are also centers of excellence in medical research and healthcare. Graduating from any of these institutions can open doors to become a doctor in India and gear you for a successful career.
Comparison of government sector vs. private sector MBBS colleges in India
Feature | Government colleges | Private colleges |
Average annual tuition fee | ₹10,000 - ₹50,000 | ₹7,00,000 - ₹20,00,000 |
Additional costs | ₹20,000 - ₹50,000 (Hostel, Exam Fees, etc.) | ₹1,00,000 - ₹2,00,000 (Hostel, Exam Fees, etc.) |
Total annual cost (approx.) | ₹30,000 - ₹1,00,000 | ₹8,00,000 - ₹22,00,000 |
Pros | - Lower Tuition Fees | - Better Infrastructure and Facilities |
Cons | - Limited Seats | - High Tuition Fees |
This table provides a comprehensive overview of the key differences between government and private colleges, helping prospective students evaluate their options.
Top MBBS colleges in India
Rank | College name | Location | Total seats | Average NEET cut-off (2023) | Notable features |
1 | All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) | New Delhi | 107 | 720-730 | Prestigious, High Research Output, Top Faculty |
2 | Maulana Azad Medical College (MAMC) | New Delhi | 250 | 710-725 | Well-Established, High Clinical Exposure |
3 | Armed Forces Medical College (AFMC) | Pune | 130 | 680-700 | Exclusive for Armed Forces, Rigorous Training |
4 | Christian Medical College (CMC) | Vellore | 100 | 700-715 | Renowned for Rural Health Services |
5 | Kasturba Medical College (KMC) | Manipal | 250 | 690-705 | Excellent Infrastructure, International Students |
6 | JIPMER (Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research) | Puducherry | 200 | 680-695 | Focus on Research and Community Health |
7 | King George's Medical University (KGMU) | Lucknow | 250 | 685-700 | Strong Academic and Clinical Programs |
8 | Government Medical College (GMC) | Nagpur | 150 | 670-685 | Good Clinical Exposure, Government-Aided |
9 | Indira Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences (IGIMS) | Patna | 100 | 665-680 | Growing Reputation, Increasing Research Output |
10 | Sri Ramachandra Medical College | Chennai | 250 | 675-690 | Advanced Facilities, Strong Clinical Training |
11 | Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER) | Chandigarh | 100 | 700-720 | Leading Medical and Research Institution, Specialized Training |
Admission process and fee payment
The admission process to MBBS colleges in India is primarily based on the NEET exam scores. After the results are announced, candidates must participate in the counseling process, where they can select their preferred colleges based on their NEET rank. The counseling process is conducted in multiple rounds, and candidates are allotted seats in medical colleges based on their preferences, rank, and availability of seats.
Once you have been allotted a seat, the next step is to complete the fee payment process. The fee structure for medical colleges in India varies widely depending on whether the institution is government-run or private. Government medical colleges generally have lower fees compared to private colleges. However, private colleges may offer better infrastructure and facilities. Make sure you're not just considering the fees but also the value you'll get from the program.
Beyond tuition fees, you’ll also need to budget for things like hostel accommodation, textbooks, and other everyday expenses. Scholarships and financial aid are available for deserving candidates, so it's worth exploring these options if you need financial support.
Step 4: Completing the MBBS degree
Structure of the MBBS program
The MBBS program in India is a rigorous five-and-a-half-year course, including a compulsory internship. The MBBS course is divided into three main phases:
- Pre-clinical phase: This phase covers the basic sciences, including subjects like Anatomy, Physiology, and Biochemistry. These subjects are all about learning how the human body is built and how it functions.
- Para-clinical phase: In this phase, students are introduced to subjects like Pathology, Microbiology, Pharmacology, and Forensic Medicine. These subjects help students get to grips with how diseases work, how germs cause illness, and how medicines help treat them.
- Clinical phase: The final phase involves hands-on training in various clinical subjects, including Medicine, Surgery, Pediatrics, Obstetrics & Gynecology, and Psychiatry. In this phase, students roll up their sleeves and work directly with real patients, learning how to diagnose and treat issues firsthand.
The MBBS course is all about giving you the tools you need to practice medicine confidently.
One year internship: gaining practical experience
The one-year internship is a key part of your MBBS program and it's something MBBS students have to complete. It’s your chance to dive into real medical work, applying everything you’ve learned so far. You’ll work with experienced doctors in various departments like General Medicine, Surgery, Pediatrics, Obstetrics & Gynecology, and Emergency Medicine.
This mandatory internship is not just a requirement; it’s a golden opportunity to get hands-on experience, sharpen your clinical skills, and see what the medical profession is really like. It’s also a great way to explore different specialties and figure out what career path suits you best.
Step 5: Obtaining your medical license
National Medical Council (NMC) and State medical councils
To legally practice medicine in India, you must obtain a medical license from the NMC or the respective State Medical Council. The medical license is a legal requirement that ensures that only qualified and competent individuals are allowed to practice medicine.
After completing your MBBS degree and internship, you must apply for registration with the MCI or the State Medical Council in the state where you intend to practice.To get your medical license, you’ll need to submit your academic credentials, internship completion certificate, and a few other documents. Once everything’s approved, you'll receive a registration certificate, which lets you practice medicine in India.
This license isn’t just a formality; it confirms that you’re qualified to care for patients. It also comes with responsibilities like following ethical standards, keeping patient information confidential, and staying updated with continuing medical education (CME) to keep your skills sharp.

Step 6: Pursuing postgraduate specialization (optional)
Options for further studies
While an MBBS degree allows you to practice medicine as a general practitioner, many doctors choose to pursue further specialization in a particular area of medicine. Postgraduate specialization allows you to develop expertise in a specific field and opens up opportunities for advanced clinical practice, research, and teaching.
There are several options for postgraduate medical studies in India, including:
- Doctor of Medicine (MD): This is a postgraduate degree in medicine that focuses on a particular specialty, such as Internal Medicine, Pediatrics, or Radiology. The MD program typically lasts for three years and involves advanced clinical training and research in the chosen specialty.
- Master of Surgery (MS): This is a postgraduate degree in surgery that allows doctors to specialize in areas such as General Surgery, Orthopedics, or Obstetrics & Gynecology. Like the MD program, the MS program also lasts for three years.
- Diploma courses: In addition to MD and MS programs, there are also various diploma courses available in different medical specialties. These courses are typically shorter in duration (two years) and provide focused training in a specific area of medicine.
Importance of NEET-PG exam
To gain admission to a postgraduate medical program in India, you must clear the NEET-PG exam. The NEET-PG exam is a national-level entrance test that assesses your knowledge and understanding of the subjects covered during your MBBS course. The exam is highly competitive, and securing a good rank is essential for getting into a reputed postgraduate medical program.
The NEET-PG exam covers a wide range of topics, including clinical, pre-clinical, and para-clinical subjects. It is essential to start preparing early and adopt a focused study plan to cover the entire syllabus. Joining a coaching institute for NEET-PG preparation can also be beneficial, as it provides structured guidance and practice tests to help you succeed.
Step 7: Exploring career opportunities
Working in hospitals and clinics
After obtaining your medical license, you can start your career as a medical practitioner. Starting out in hospitals, clinics, or healthcare centers is a common path for many doctors. This gives you experience to not only treat patients from all walks of life, and let you grow your skills but also to work closely with nurses, pharmacists, and specialists to give the best care possible.
Starting your private practice
If you like the idea of working independently, a private practice might be perfect for you.
It’s not without its challenges, though. You'll have to handle things like finances, staff, and compliance with regulations. But many find it rewarding because it allows for a personal touch with patients and can lead to higher earnings, especially if you specialize in a high-demand area
Opportunities in medical research and academia
Picture yourself working on exciting projects to find new treatments or understanding diseases better, often alongside universities or drug companies. If this excites you, then a career in medical research might be right for you.
To some it's also satisfying to help shape the next generation of doctors by teaching at a medical school. You’d get to mentor students, work on impactful research, and play a role in the future of medicine. Both options let you stay connected to the heart of healthcare and make a real difference.

Average doctor's salary in India
Specialization | Average annual salary (INR) |
General Practitioner | ₹6,00,000 - ₹10,00,000 |
Pediatrician | ₹8,00,000 - ₹12,00,000 |
Surgeon | ₹10,00,000 - ₹20,00,000 |
Cardiologist | ₹15,00,000 - ₹30,00,000 |
Orthopedic Surgeon | ₹12,00,000 - ₹25,00,000 |
Gynecologist | ₹8,00,000 - ₹15,00,000 |
Neurologist | ₹12,00,000 - ₹22,00,000 |
Oncologist | ₹15,00,000 - ₹35,00,000 |
Radiologist | ₹10,00,000 - ₹20,00,000 |
Anesthesiologist | ₹10,00,000 - ₹18,00,000 |
Salaries vary by experience, location, and type of healthcare facility.
Conclusion: The rewarding journey of becoming a doctor in India
To become a doctor in India requires a lot of sacrifice but it is as rewarding. You need alongside hardworking and dedication, a true passion to help others. From preparing for the NEET exam to picking the right medical college, completing your MBBS degree, and getting your medical license, each step is vital in shaping your future as a medical professional. However, worry not! NEETsheet by futureMBBS is dedicated to making your dreams come true, offering high-quality preparation with resources from India’s best Ed-Tech teachers!
To become a doctor in India is no less than a to be a messiah who has the chance to truly impact the lives of people, and ease their suffering while contributing positively to the society at large. The sense of fulfillment and purpose you get from this career apart from professional growth is unmatched.
Click here to download the NEET Botany chapter-wise weightage
Download PDFFREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
FAQs about how to become a doctor in India
What qualifications do I need for MBBS admission in India?
You need a Class 12 pass with 50% in Physics, Chemistry, and Biology, and a valid NEET UG score.
How does NEET affect my MBBS prospects?
NEET is the mandatory entrance test for MBBS admissions in India and is required for all medical colleges. With NEETsheet by futureMBBS you are sure to ace this exam!
What’s the best way to prepare for NEET effectively?
Concentrate on NCERT textbooks, practice past papers, and take regular mock tests.
What’s the difference between government and private medical colleges in terms of fees?
Government colleges have lower fees and high competition, while private colleges charge more but offer better amenities.
What can I do after finishing my MBBS degree?
You can practice as a doctor, specialize further, pursue MD/MS, engage in research, or teach in medical schools.