☝️ At a glance
- Complete secondary education – Study Physics, Chemistry, and Biology in high school and clear medical entrance exams like NEET (India) or IMAT (Italy) for MBBS admission.
- Earn a medical degree (MBBS/MD) – Enroll in a 5-6 year medical program in India or Europe, covering anatomy, pathology, and surgical care, with clinical training.
- Specialize in ENT – After MBBS, pursue MS ENT (India) or Residency (Europe), typically lasting 3-6 years, focusing on ENT surgeries and treatments.
- Obtain licensure & certification – Pass licensing exams like NEET-PG (India) or LEK (Poland) to gain board certification and practice as an ENT specialist.
- Start your career in ENT – Work in hospitals, private clinics, research institutions, or academic settings, with opportunities in pediatric ENT, neurotology, plastic surgery, and more.
Introduction
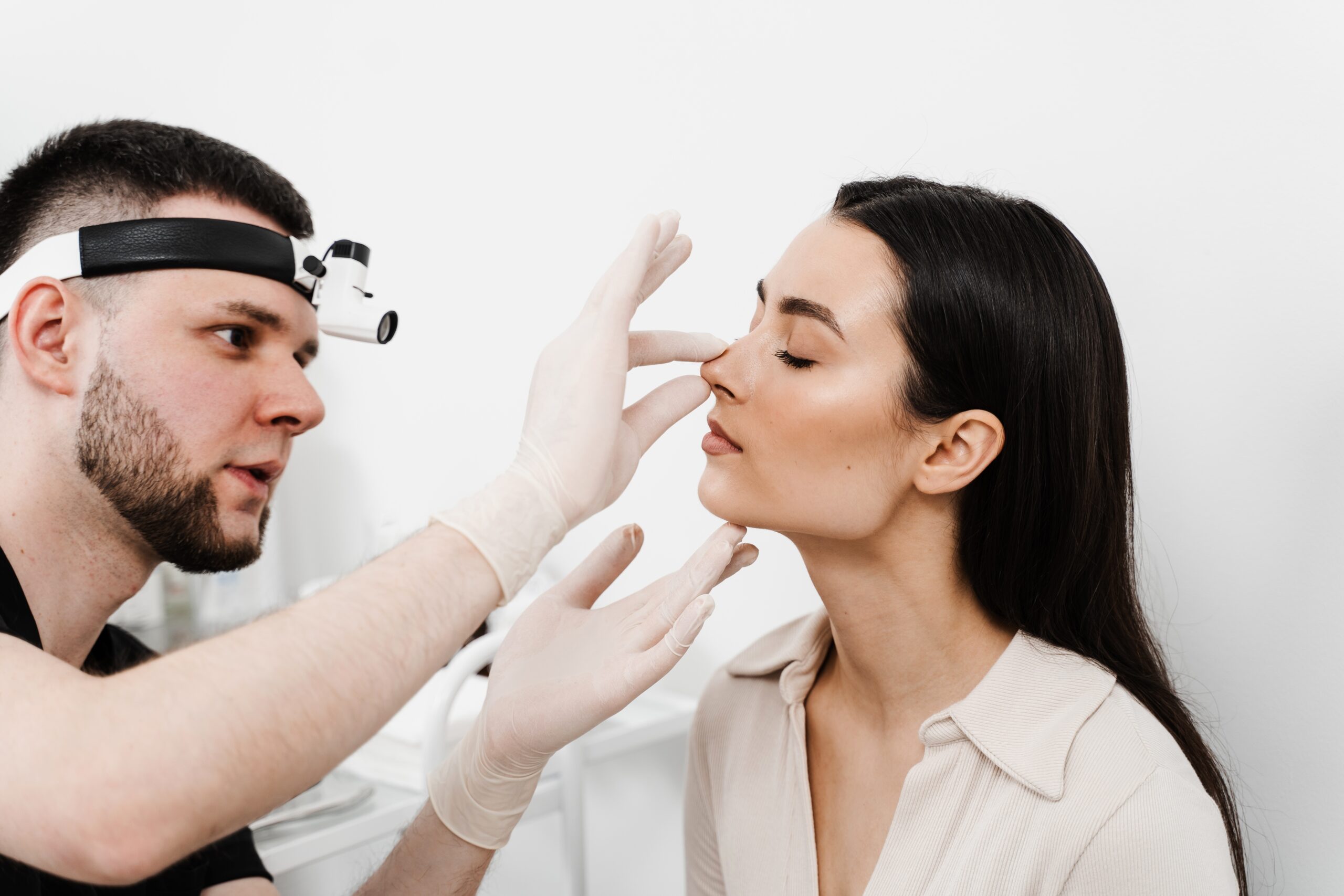
An ENT doctor, also known as an Otolaryngologist, is a medical specialist who diagnoses and treats conditions related to the ear, nose, throat (ENT), head, and neck. ENT doctors perform ear surgeries, throat surgeries, plastic surgery, skull base surgery, and reconstructive surgeries for various disorders. They also treat conditions like hearing loss, chronic sinusitis, sleep apnea, voice disorders, and nerve pathway disorders.
Becoming an ENT specialist requires years of dedicated medical education, specialty training, board certification, and hands-on experience in performing surgical procedures. This guide explains the step-by-step process, entrance exams, best medical schools, job roles, salary expectations, and career opportunities for aspiring ENT doctors.

Become a global doctor with MBBS abroad!
Studying abroad can be affordable and stress-free with futureMBBS:
- World-recognized universities with English-taught programs
- On-site support in partner university cities
- Guaranteed placements & internships for hands-on experience
From selecting universities and supporting you with the application process to orientation and finding accommodation – we are at your side.
Who is an ENT doctor?
An ENT doctor, also known as an otolaryngologist, is a medical specialist who diagnoses and treats conditions affecting the ear, nose, throat (ENT), head, and neck. They manage a wide range of disorders, including hearing loss, chronic sinusitis, sleep apnea, balance disorders, nerve pathway disorders, and throat conditions. ENT specialists can further specialize in areas like pediatric ENT, facial plastic surgery, skull base surgery, and reconstructive procedures.
ENT doctors work in hospitals, outpatient clinics, research institutions, and private practices. They are responsible for treating conditions such as middle ear infections, voice disorders, nasal passage blockages, salivary gland diseases, and head & neck tumors. ENT specialists often collaborate with plastic surgeons, neurologists, speech-language therapists, and oncologists to provide multidisciplinary care.
Job role of an ENT doctor
ENT doctors perform a variety of diagnostic and surgical procedures to treat disorders related to the ear, nose, throat, head, and neck. Their primary responsibilities include:
1. Diagnosing and treating ENT disorders
Treat ear conditions such as hearing loss, nerve pain, balance disorders, and chronic infections.
Manage nasal passage disorders like chronic sinusitis, deviated septum, and breathing problems.
Address throat conditions including tonsillitis, voice disorders, and swallowing difficulties.
Treat head and neck tumors, both benign and malignant.
2. Performing surgical procedures
Conduct cochlear implants for hearing restoration.
Perform skull base surgery for treating complex brain-related ENT conditions.
Carry out cleft lip correction and facial plastic surgery.
Perform reconstructive surgeries for trauma, birth defects, or cancer recovery.
3. Working with multidisciplinary teams
Collaborate with plastic surgeons, speech-language therapists, and oncologists.
Assist in the rehabilitation of patients with nerve pathway disorders and communication difficulties.
4. Providing post-surgical care and rehabilitation
Offer surgical care for nerve pain, salivary gland disorders, and breathing problems.
Refer patients for additional treatments like speech therapy and nerve rehabilitation.
ENT doctors play a vital role in improving hearing, breathing, speech, and overall quality of life, making them essential in both medical and surgical fields.
How to become an ENT doctor?
Becoming an ENT (ear, nose, and throat) specialist, also known as an otolaryngologist, involves completing medical education, specialized training, and obtaining licensure. ENT doctors diagnose and treat conditions related to the ear, nose, throat, head, and neck through medical and surgical interventions.
The process varies slightly between India and Europe, but the general pathway remains consistent.
Step 1: Complete secondary education with science (physics, chemistry, biology)
Aspiring ENT specialists must complete higher secondary education (10+2) with physics, chemistry, and biology. A strong foundation in these subjects is essential for pursuing medical education.
Step 2: Clear medical entrance examinations
Admission to medical schools requires clearing competitive entrance examinations. The specific exams depend on the country of study.
Exam name | Country | Purpose | Conducting body |
|---|---|---|---|
NEET-UG | India | MBBS admission | National Testing Agency (NTA) |
IMAT | Italy | Medical school admission | Italian Ministry of Education |
HAM-Nat | Germany | Public medical school admission | German Medical Council |
Step 3: Obtain a medical degree (MBBS or MD)
After clearing entrance exams, students enroll in a medical degree program. The duration and nomenclature of the degree vary by country.
Country | Degree awarded | Duration |
|---|---|---|
India | MBBS | 5.5 years |
Lithuania | MD | 6 years |
Hungary | MD | 6 years |
Slovakia | MD | 6 years |
Latvia | MD | 6 years |
Cyprus | MD | 6 years |
Poland | MD | 6 years |
Croatia | MD | 6 years |
Romania | MD | 6 years |
Czech Republic | MD | 6 years |
During this period, medical students study subjects like medical sciences, anatomy, pathology, pharmacology, and surgical care. They also gain hands-on clinical experience.
Step 4: Pursue postgraduate specialization in ENT
After obtaining a medical degree, doctors must pursue postgraduate training in ENT specialization.
Exam name | Purpose | Country |
|---|---|---|
NEET-PG | Admission to MS ENT | India |
Facharzt | Specialization in ENT | Germany and other European countries |
In India, students clear NEET-PG to gain admission to MS ENT (Master of Surgery in ENT) or DNB ENT (Diplomate of National Board in ENT). These programs last 3 years and focus on advanced surgical procedures and treatments.
In Europe, specialization is done through residency training. For example, in Germany, students must complete the Facharztausbildung, which takes 5-6 years and includes extensive clinical rotations and surgical experience.
Step 5: Obtain licensure and board certification
After completing ENT specialization, doctors must obtain board certification and medical licenses to practice independently.
Country | Medical licensing exam | Regulatory body |
|---|---|---|
India | NEET-PG | National Medical Commission (NMC) |
Lithuania | Medical licensing exam | Lithuanian Medical Council |
Hungary | State medical exam | Hungarian Medical Council |
Slovakia | National licensing exam | Slovak Medical Association |
Latvia | National exam for medical practice | Latvian Medical Council |
Cyprus | Cyprus medical licensing | Cyprus Medical Association |
Poland | LEK exam | Polish Chamber of Physicians |
Croatia | National licensing exam | Croatian Medical Association |
Romania | Residency exam | Romanian Ministry of Health |
Czech Republic | National exam | Czech Medical Chamber |
In India, graduates register with the National Medical Commission (NMC). In Europe, each country has its own licensing examination and regulatory council. Some European countries also require proficiency in the local language.

Study medicine abroad with 100% support!
futureMBBS offers full support to make your dream of studying medicine abroad a reality.
- Hassle-free admission guidance
- Fast-tracked visa processing
- Post-arrival support, including accommodation assistance
Step 6: Begin practice as an ENT specialist
After obtaining board certification, ENT doctors can start their careers in hospitals, private clinics, or research institutions.
Roles and responsibilities of an ENT specialist
Diagnosing and treating conditions related to the ear, nose, throat, head, and neck
Performing surgical procedures like cochlear implants, skull base surgery, cleft lip correction, and reconstructive surgeries
Working with multidisciplinary teams, including plastic surgeons, language therapists, and other physicians
Providing surgical care for nerve pain, salivary gland disorders, birth defects, and breathing problems
Referring patients for additional treatments, such as speech-language therapy and nerve pathway rehabilitation
Subspecialties in ENT
Some ENT specialists pursue further subspecialization in specific areas such as:
Pediatric otolaryngology – Treating ENT conditions in children
Neurotology – Managing ear and skull base disorders
Facial plastic and reconstructive surgery – Performing facial plastic surgery and reconstructive procedures
Laryngology – Specializing in voice disorders and throat conditions
Head and neck surgery – Treating head and neck tumors, nerve pathway disorders, and balance disorders
Career opportunities for ENT specialists in India and Europe
ENT doctors have a wide range of career opportunities in both India and European countries.
In India:
Government sector – Working in AIIMS, PGIMER, state-run hospitals, and medical colleges
Private sector – Joining private hospitals, corporate healthcare chains, and outpatient clinics
Academia and research – Teaching in medical schools and conducting clinical research
Private practice – Opening an independent ENT clinic
In Europe:
Hospitals and clinics – Working in government and private healthcare institutions
Academic and research institutions – Conducting advanced research in ENT and related fields
Subspecialty fellowships – Pursuing further training in facial plastics, reconstructive surgeries, and skull base surgery
Medical tourism – Working in countries like Hungary, Poland, and Lithuania, which attract patients from across Europe for affordable yet high-quality ENT treatments.
Top medical schools for ENT specialization in India and Europe

University | Country | Programs Offered |
|---|---|---|
AIIMS Delhi | India | MS ENT, DNB ENT |
University of Health Sciences Kaunas | Lithuania | MD + ENT Residency |
Semmelweis University | Hungary | MD + ENT Specialization |
Jessenius University | Slovakia | ENT Residency |
Stradins University Riga | Latvia | MD + ENT Residency |
University of Nicosia | Cyprus | ENT Specialization |
Medical University Poznan | Poland | MD + ENT Residency |
University of Split | Croatia | ENT Residency |
Medical University Cluj | Romania | MD + ENT Residency |
Charles University | Czech Republic | ENT Specialization |
Salary and job outlook for ENT doctors
Country | Average Annual Salary (€) | Equivalent in INR (₹) |
|---|---|---|
India | ₹10,00,000 – ₹30,00,000 | ₹10-30 LPA |
Lithuania | €60,000 – €120,000 | ₹50-100 LPA |
Hungary | €70,000 – €130,000 | ₹60-110 LPA |
Slovakia | €60,000 – €110,000 | ₹50-90 LPA |
Latvia | €50,000 – €100,000 | ₹45-85 LPA |
Cyprus | €55,000 – €105,000 | ₹50-95 LPA |
Poland | €65,000 – €125,000 | ₹55-105 LPA |
Croatia | €50,000 – €100,000 | ₹45-85 LPA |
Romania | €55,000 – €110,000 | ₹50-90 LPA |
Czech Republic | €70,000 – €130,000 | ₹60-110 LPA |
High demand for ENT specialists in hospitals, research, medical sciences, and government sector jobs.
Conclusion
Becoming an ENT doctor in India or Europe requires years of rigorous education, training, and licensing. ENT specialists play a vital role in diagnosing and treating conditions related to the ear, nose, throat, head, and neck. They perform surgeries, treat hearing disorders, improve speech, and manage life-threatening conditions such as throat cancer and airway obstructions.
For students aspiring to pursue MBBS in Europe, futureMBBS is the leading consultancy that provides end-to-end assistance for admission, visa processing, university selection, and post-arrival support. With partnerships in 19+ top medical universities across Europe, futureMBBS ensures students receive world-class education, clinical exposure, and affordable tuition fees compared to private colleges in India.
If you aim to study MBBS in India, cracking NEET is the first step. NEETsheet by futureMBBS is an advanced preparation platform designed to help students ace the NEET exam with expert curated study materials, mock tests, time management strategies, and personalized coaching. With a proven track record of success, NEETsheet equips students with the knowledge and strategies needed to secure admission into India’s top medical colleges.
Ready to start your journey to becoming an ENT doctor? Contact futureMBBS today for expert guidance on MBBS admissions in India and Europe!
Thinking of pursuing MBBS abroad? Don’t just dream it, do it!Your medical career abroad starts here!
Read more similar articles:
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
FAQs about “becoming an ENT doctor"
Can I do ENT without MBBS?
No, you cannot become an ENT doctor without completing an MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery) or equivalent MD degree. ENT specialization is a postgraduate course that requires a basic medical degree. However, if you are interested in working in the ENT field without an MBBS, you can pursue roles like audiologist, speech therapist, or ENT technician.
How many years does it take to become an ENT specialist?
Becoming an ENT specialist typically takes 8 to 12 years, depending on the country and education pathway:
MBBS/MD degree – 5 to 6 years
Postgraduate ENT specialization (MS ENT, DNB ENT, or equivalent) – 3 to 5 years
Fellowships or super-specialization (optional) – 1 to 3 years
How many years is an ENT course?
The ENT course duration depends on the level of study:
Undergraduate (MBBS/MD degree) – 5 to 6 years
Postgraduate (MS ENT/DNB ENT/Residency) – 3 to 5 years
Super-specialization/Fellowships – 1 to 3 years
Is NEET necessary for ENT?
Yes, NEET is necessary for pursuing ENT specialization in India. Here’s where it is required:
NEET-UG – Required for MBBS admission
NEET-PG – Required for MS ENT admission
No NEET required for foreign universities in some European countries (e.g., Romania, Croatia, Latvia), but their own entrance exams may be required.




