☝️ At a glance
- Forensic science applies scientific methods to solve crimes by analyzing evidence from crime scenes.
- To become a forensic expert, pursue B.Sc, MSc., or Ph.D. in Forensic Science or MBBS followed by MD in Forensic Medicine.
- Forensic experts collect, analyze evidence, assist in investigations, and testify in court.
- Entry-level salaries range from ₹2.5 to 4.5 LPA, with senior roles earning up to ₹15 LPA.
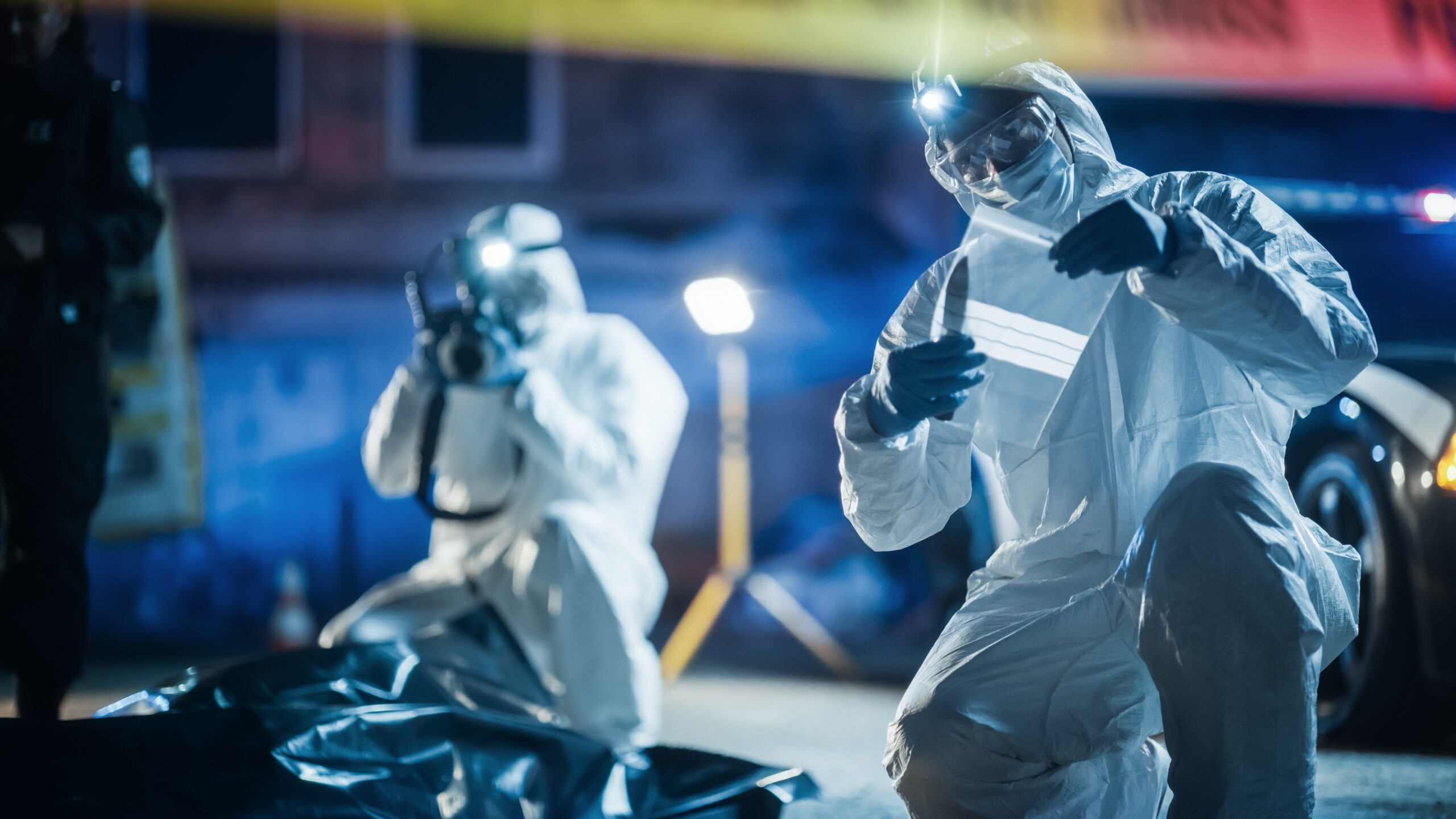
Do you love crime or detective movies and have a knack for solving mysteries? If so, forensic science might be the perfect career for you!
Forensic science is all about using scientific techniques to help solve crimes, providing key evidence for investigations. Whether it’s a murder case, drug trafficking, or even civil issues like pollution, forensic experts play a crucial role in bringing facts to light. It’s a fascinating field that blends science and law, helping to crack cases and support justice. If you’re curious about pursuing a career in forensic science, this article will walk you through everything you need to know to get started on this exciting path.

Become a global doctor with MBBS abroad!
Studying abroad can be affordable and stress-free with futureMBBS:
- World-recognized universities with English-taught programs
- On-site support in partner university cities
- Guaranteed placements & internships for hands-on experience
From selecting universities and supporting you with the application process to orientation and finding accommodation – we are at your side.
Forensic medical science course overview
Particulars | Details |
Course Levels | Undergraduate (UG), Postgraduate (PG), Doctorate |
Duration | 2-3 years |
Course Fees | ₹2,000 – ₹21,00,000 |
Admission Criteria | UG: Merit-Based · PG: Entrance-Based |
Eligibility | - Class 12 with Science (Physics, Chemistry, Biology) and 50% marks |
| Other eligibility criteria | - Some institutes accept Botany, Computer Science, Biochemistry, or Zoology as major subjects in Class 12 |
Entrance Exam | NEET PG (for Postgraduate courses) |
Popular Colleges | JIPMER, KMC, SRIHER, JSS Medical College, SMS Medical College, and others |
Job Roles | DNA Analyst, Forensic Pathologist, Forensic Toxicologist, Forensic Odontologist, etc. |
Average Salary | Entry-level: ₹2.5–4.5 LPA · Mid-level: ₹4.5–8 LPA · Senior-level: ₹8–15 LPA |
Top Recruiters | Police and CBI, State Forensic Labs, Regional/District Forensic Science Labs, Protective Services, etc. |

Study medicine abroad with 100% support!
futureMBBS offers full support to make your dream of studying medicine abroad a reality.
- Hassle-free admission guidance
- Fast-tracked visa processing
- Post-arrival support, including accommodation assistance
Roles and responsibilities of a forensic scientist
- Collect, identify, classify, and analyze physical evidence from crime scenes.
- Preserve evidence by storing it properly and perform tests on items like fibers, hair, and weapons.
- Testify as an expert witness in court on evidence and laboratory methods.
- Prepare detailed reports on findings, methods, and techniques used in investigations.
- Document crime scenes using photography or video.
- Visit crime scenes or morgues and collaborate with other experts to gather information.
- Reconstruct crime scenes to understand how evidence relates.
- Operate and maintain lab equipment and prepare necessary solutions.
- Consult with specialists in areas like ballistics, fingerprinting, or chemistry.
- Examine latent fingerprints using chemicals and compare them to known prints in databases.
Why study forensic science?
Solve crimes: Forensic science helps solve crimes by analyzing evidence, which is crucial for uncovering the truth and ensuring justice is served.
Diverse career opportunities: It offers a range of specializations, such as toxicology, ballistics, and DNA analysis, providing various career paths within law enforcement, government agencies, and private labs.
Impactful work: Forensic scientists utilize medical sciences and play a key role in criminal investigations and legal proceedings, making a tangible impact on public safety and the criminal justice system.
Scientific challenge: The field combines scientific techniques with investigative skills, offering a stimulating and intellectually rewarding career for those interested in science and problem-solving.
How to become a forensic scientist in India
To pursue a career as a forensic scientist in India, you need to follow specific educational pathways and meet certain eligibility criteria and qualifications. There are three ways to become a forensic scientist:
Pathway 1:
- Complete Class 12 with a Science background.
- Obtain a B.Sc. in Forensic Science.
- Pursue an M.Sc. in Forensic Science.
- Optionally, complete a Ph.D. in Forensic Science for advanced research or academic roles.
Pathway 2:
- Complete Class 12 with a Science background.
- Obtain a B,Sc. in Forensic Science.
- Proceed with a PG Diploma in Forensic Science.
Pathway 3:
- Complete Class 12 with a Science background.
- Obtain an MBBS degree.
- Pursue an MD in Forensic Medicine (MD forensic medicine).
Courses and duration
Course | Duration |
B.Sc. in Forensic Science | 3 years |
M.Sc. in Forensic Science | 2 years |
PG Diploma in Forensic Science | 1-2 years |
Ph.D. in Forensic Science | 3 years |
MPhil in Forensic Science | 3 years |
Admission criteria and fees
Eligibility: Complete Class 12 with Physics, Chemistry, and Biology with at least 50% marks. Some colleges accept Botany, Computer Science, Biochemistry, or Zoology as alternatives.
- UG admission: Based on Class 12 scores.
- PG admission: Based on NEET PG scores.
- Course fees: Range from INR 2,000 to INR 21 Lakh depending on the institution and course level.
Key skills required for forensic science

Chemistry: Understanding chemical processes and reactions is fundamental for analyzing substances.
Human anatomy: A thorough knowledge of human anatomy is also required.
Data Analysis: Interpreting data and results accurately to draw meaningful conclusions.
Chromatography: Techniques for separating and analyzing compounds in a mixture.
Electron Microscopy and DNA Profiling: Advanced methods for examining samples at a microscopic level and identifying genetic material.
Career opportunities in forensic science
Forensic scientist: Conducts comprehensive analyses of evidence.
Forensic specialist: Provides expert knowledge in specific areas of forensic science.
Crime scene investigator (CSI): Collects and examines evidence from crime scenes.
Crime scene analyst: Analyzes crime scene data to support investigations.
Crime scene technician (Crime Scene Tech): Assists in the collection and preservation of evidence.
Evidence technician: Manages and processes evidence collected during investigations.
Forensic science examiner: Examines and interprets forensic evidence.
Latent fingerprint examiner: Analyzes fingerprint evidence.
Crime laboratory analyst: Performs tests and analyzes results in a forensic lab.
Top colleges for forensic science in India
Top colleges (government) offering forensic medical science courses
Several government institutions in India provide Forensic Medical Science programs. Here are some of the notable ones:
College | Course Fees |
JIPMER Puducherry | INR 46,600 |
S.M.S. Medical College | INR 2,000 - 18,100 |
Madras Medical College | INR 1.5 Lakh |
Armed Forces Medical College | INR 3.9 Lakh |
MUHS | INR 8,200 |
Grant Medical College | INR 1.5 Lakh |
Kaloji Narayana Rao University of Health Sciences | INR 20.7 Lakh |
RajaRajeswari Medical College and Hospital | INR 18 Lakh |
Rashtriya Raksha University | INR 2 Lakh |
Top colleges (private) for forensic medical science courses
There are 18 private colleges offering forensic medical science courses. Some of the notable institutions include Kasturba Medical College, Sri Ramachandra Institute of Higher Education and Research, and JSS Medical College. Below are details of popular private colleges and their course fees:
College | Course Fees |
Kasturba Medical College, Manipal | INR 3 Lakh - 10.9 Lakh |
Sri Ramachandra Institute of Higher Education and Research | INR 21 Lakh |
JSS Medical College | INR 18.2 Lakh |
Suresh Gyan Vihar University | INR 2 Lakh |
NIMS University | INR 90,000 - 1.8 Lakh |
Jaipur National University | INR 1.4 Lakh |
Rayat Bahra University | INR 1 Lakh |
K.S. Hegde Medical Academy | INR 5.5 Lakh |
Adamas University | INR 2.8 Lakh |
Specializations in forensic science
Forensic science is a diverse field encompassing various specializations, each focusing on different aspects of crime analysis and investigation. Here are some key areas of expertise:
DNA analysis: Examines genetic material to establish identities, relationships, and connections between individuals and crime scenes.
Forensic toxicology: Analyzes body fluids, tissues, and organs to detect drugs, alcohol, poisons, and other substances, crucial for drug-related cases and incidents involving unknown substances.
Ballistics and firearms examination: Investigates bullets, shell casings, firearms, and ammunition to determine if a specific weapon was used in a crime, including analyzing bullet trajectories and firearm markings.
Forensic chemistry: Studies substances such as drugs, explosives, and trace evidence from crime scenes to determine their composition and relevance to criminal investigations.
Forensic pathology: Forensic pathologists conduct autopsies to identify the cause and manner of death in cases of suspicious or unexplained deaths, determining if a death was due to natural causes, accidents, suicide, or foul play. You can become a forensic pathologist if this interests you.
Fingerprint analysis: Utilize medical science to identify unique ridge patterns on fingerprints to match prints found at crime scenes with known individuals, establishing connections between suspects and locations.
Digital and cyber forensics: Examines digital devices and electronic evidence to recover and analyze data related to cybercrimes and other digital offenses.
Forensic anthropology: Analyzes human remains to determine age, sex, ancestry, and trauma, aiding in identification and understanding the circumstances surrounding a person's death.
Forensic odontology: Reviews dental records and bite marks to identify human remains and provide expert testimony in cases involving dental evidence.
Entomology: Studies insect activity on decomposing bodies to estimate time of death and other details related to the decay process.
Forensic document examination: Analyzes documents, handwriting, signatures, and other written materials to verify their authenticity and uncover alterations or connections to criminal activities.
Fire and explosion investigation: Determines the cause and origin of fires and explosions, investigating whether they were accidental, intentional, or due to negligence.
Forensic psychology and profiling: Assesses the behavior and mental state of individuals involved in criminal cases, using behavioral analysis to create psychological profiles of suspects.
Forensic nursing: Provides medical care to victims of violence, documents injuries, collects evidence, and collaborates with law enforcement in cases of assault, abuse, and other violent crimes.
These specializations highlight the complexity and breadth of forensic science, allowing individuals to choose an area that aligns with their interests and skills in the field of criminal investigation and justice.
Major coursework structure
Forensic science program involves coursework that typically integrates scientific subjects such as biology, chemistry, and physics. Additionally, classes in statistics, criminal justice, and law provide specialized training into the legal aspects of the field. The choice of specialization will influence the specific courses you take.
Hands-on practice: Gaining practical experience is crucial. Engage in internships, research positions, or part-time roles in laboratories, law enforcement agencies, or related organizations to develop skills in conducting tests, analyzing evidence, and using advanced equipment.
Strong analytical skills: Forensic scientists must possess excellent analytical abilities. Key skills include analytical thinking, attention to detail, problem-solving, and the capability to draw logical conclusions from complex data.
Stay updated with technology: Forensic science is rapidly evolving. Keep abreast of the latest advancements in forensic tools, software, and methodologies to ensure you remain current and effective in your work.
Networking: Build a professional network by attending conferences, workshops, and seminars. Connecting with experts in the field will help you stay informed about new developments and may open doors to job opportunities.
Certifications: Although not always required, certifications can boost your credibility and career prospects. Consider programs offered by organizations such as the American Board of Criminalistics (ABC) for various forensic disciplines.
Job search: After completing your education and gaining experience, start looking for job opportunities in government agencies, law enforcement departments, private labs, and research institutions. Roles may include forensic analyst or crime scene investigator.
Application and interview process: Update your resume and cover letter to highlight relevant skills and experience. During interviews, focus on your analytical abilities, attention to detail, and dedication to accuracy. Be ready to discuss your experience with evidence handling, lab equipment, and collaboration with law enforcement.
Continuing education: The field of forensic science is continually advancing. Engage in ongoing education, workshops, and advanced training to keep up with new developments and maintain your professional edge.
Forensic medical science syllabus

The Forensic Medical Science syllabus provides a thorough grounding in both theoretical and practical aspects of forensic medicine. It includes a range of subjects designed to equip students with the essential knowledge and skills for success in forensic medical investigations. The syllabus is structured over three years, with each year focusing on different core areas.
Forensic medical science courses
Year | Subjects |
Year 1 | - Introduction to Forensic Science & Criminalities |
Year 2 | - Fundamentals of Biology |
Year 3 | - Instrumentation and Investigation Techniques |
This syllabus ensures that students gain a comprehensive understanding of forensic science, preparing them for various aspects of forensic medical practice.
Top 5 highest paying careers in forensic science
Here are the top five highest-paying careers in forensic science that aspiring professionals can pursue:
Forensic medical expert
Forensic medical experts determine the cause of death in unnatural cases. Board certification is often required, so consider enrolling in certification programs before making a decision.
Forensic expert
Forensic experts investigate machinery and design to identify causes of failure, foul play, and other criminal activities. They can expect to earn around INR 61,07,778.68.
Forensic accountant
Forensic accountants handle cases involving contract breaches, bankruptcy, fraud (including securities and tax), and business evaluations. They also examine computers and IT systems for financial crimes.
Crime scene investigator
Crime scene investigators need at least a bachelor’s degree in forensic science or a related field. The starting salary in 2015 was approximately INR 3,61,969.
Crime laboratory analyst
Crime laboratory analysts use their expertise in biochemistry and molecular biology to examine evidence like firearms, blood, DNA, and other bodily fluids.
These roles offer substantial salaries and career opportunities for those with a background in forensic science. Educational qualifications, including a bachelor’s degree, are typically required for these positions.
The pay scale of a Forensic Expert varies according to the job roles. Check the following table for a detailed pay scale of a Forensic Expert for various job roles.
Job role | Starting salary | Mid level salary | High level salary |
Crime scene examiner | Rs. 6.00 Lakhs | Rs. 9.00 Lakhs | Rs. 12.00 Lakhs per Annum |
Forensic pathologist | Rs. 3.60 Lakhs | Rs. 4.50 Lakhs | Rs. 6 Lakhs |
Crime laboratory analyst | Rs. 4.00 Lakhs | Rs. 6.50 Lakhs | Rs. 10.00 Lakhs |
Forensic IT specialist | Rs. 4.00 Lakhs | Rs. 6.00 Lakhs | Rs. 10.00 Lakhs |
Forensic psychologist | Rs. 3.60 Lakhs | Rs. 4.20 Lakhs | Rs. 6.00 Lakhs |
Your medical career abroad starts here!
Thinking of pursuing MBBS abroad? Don’t just dream it, do it!
Start your MBBS journey!
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Is a forensic expert career tough?
Yes, it is a tough medical degree because it includes the study of several other disciplines of science. It is kind of a mixture of biology, physics, and chemistry and hence becomes quite difficult.
What is the radius/scope of forensic experts in India?
As crime is increasing around the globe and data going through several stages, the demand for professionals in the field of forensic sciences is highly demanding who can check the data. From government labs to counsellors to investigations, the nation is in high need of forensic experts.
Is Biology compulsory for B.Sc. in Forensic expert?
No, Biology is not compulsory at 10+2 level for B.Sc. Forensic experts. Students who have chosen Maths are also eligible.
What are the jobs after Forensic expert studies?
Some of the job options available after completing courses in forensic expertise are Forensic Scientist, Forensic Analyst, Crime Scene Investigator, Legal Counselor, Forensic Technician, Lab Assistant, Forensic Toxicologist, Forensic Professor, etc.
What are the qualifications needed to start a course as a forensic expert?
The qualification needed is the completion of 10+2 with a minimum of 60% aggregate in the science stream.